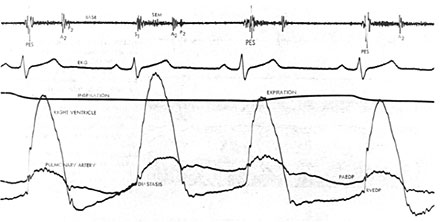
Figure 199l
Simultaneous right ventricular and pulmonary artery pressures are recorded with the phonocardiogram showing the mechanism of the attenuation of the pulmonary ejection sound (PES) during respiration in a patient with mild valvular pulmonary stenosis. In the second complex the valvular ejections sound has disappeared and there is complete equalization of the diastolic pressures in the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. With equalization of the pressure there is preopening of the deformed stenotic valve and with the onset of right ventricular systole no further excursion of the domed valve is possible, and the ejection sound is absent.During expiration, the pulmonary diastole pressure is significantly higher than the right ventricular end-diastolic pressure, and the prominent ejection sound is a gain recorded. Considerable the variation of the ejection sound occurs during various phases of respiration and is caused by varying degrees of preopening of the valve. Note the tendency of the ejection sound to occur later during the expiratory phase.